KYC and AML are acronyms for Know Your Customer and Anti-money Laundering and refer to the set of activities that both financial institutions and regulated businesses must perform to verify the identity of their customers and obtain sensitive information from them as well as prevent money laundering from illegal activities. The terms KYC / AML are also used to define the different regulations governing these activities.
A deeper knowledge of the tricks used by money laundering networks, as well as a growing public concern about the subject, has resulted in a series of changes in international standards and legislation.
As a result, there is a growing social awareness of the need to prevent all types of corruption and the financing of illegal activities such as terrorism or drug trafficking.
Preventing criminal organisations from using banking for money laundering purposes has led governments to legislate and establish procedures aimed at increasing security, both in the physical and digital world, with the ultimate responsibility of financial institutions or regulated companies to implement and adopt KYC solutions.
Nevertheless, if KYC in the financial sector was the origin at a regulatory level, affecting banks, insurance companies or export credit agencies. In that case, other industries have echoed the need to verify the identity of customers to prevent identity theft fraud through new regulations.
Examples of new industries that have been introducing KY/AML policies are the online gaming sector, cryptocurrency, betting, and telecommunications … so we could also talk about KYC in online games or cryptocurrency KYC.
But what is KYC, and what is it for?
KYC is the process that determines that the relationship between a customer and a company is secure. To this purpose, a series of technical and security controls are performed. As part of the process, a verification of the customer’s identity is included to ensure that the customer is who they claim to be.
To assess the suitability of the relationship between the parties, it is not only necessary to simply carry out an ID verification but also to incorporate facial biometrics with liveness detection and identification of the customer on AML lists such as PEP.
Therefore, it is essential to verify the real identity of the customer through a series of controls and to share the information with the Administration.

KYC identity verification process: Compliance and requirements
Currently, the KYC concept is closely linked to Digital Onboarding, and it is usually in the first stage of the relationship with the customer (Digital Onboarding) when the customer signs up or registers in the system, so KYC checks are implemented to verify their identity.
In some industries, such as Online Gaming, the obligation for ID verification by gaming operators was done at a later stage when the player wanted to withdraw their winnings. Nevertheless, regulations have become more restrictive, requiring new players to have their identity verified during the onboarding process.
Therefore, depending on the industry and the regulations that apply, different requirements are usually imposed during the registration process.
KYC/AML checks typically include the following:
- Collect and analyse basic identity information, such as identity documents. A passport, driving licence, national identity card or certificate of citizenship are generally valid.
- Verify the customer’s physical address. It is usually verified by providing utility bills such as gas, electricity or telephone, tax receipts, and bank statements.
- Check against third-party lists (PEP, police databases to check for criminal offences and problem gambling).
- Customer risk in terms of propensity to commit money laundering, terrorist financing or identity theft.
- Create an expectation of a customer’s transactional behaviour.
- Track of a customer’s transactions.
- Verify the origin of payments.
Adding Digital Onboarding to the KYC process
As mentioned, KYC and Digital Onboarding are closely linked. Digital Onboarding is the process that allows a customer to register for the first time remotely from any device (smartphone, tablet, computer) with an identity document that identifies them and verifies that they are who they claim to be.
In the banking industry, until a couple of years ago, opening a bank account required going in person to a branch so that an agent could verify the customer’s identity, so its face-to-face nature characterised the onboarding model.
As time goes by, the onboarding process has been digitised, enabling forms and agreements to be downloaded from the bank’s website until reaching the current model, in which banks have the permission of the regulatory bodies and the necessary technology to allow the customer’s first contact with the bank to be 100% digital.
The change came in May 2015 when SEPBLAC authorised the digital onboarding process through a video call. The customer showed a supporting identity document in front of their computer’s webcam or via their mobile device.
The German bank N26 was a pioneer in the implementation of Digital Onboarding in Spain. Since then, many companies from multiple industries have been using document scanning OCR technology to extract information from the identity document and biometric recognition to verify the identity of the holder of the document, integrating all the customer information generated during the process into their systems (ERP, CRM).
Nevertheless, the challenge we face in the Digital Onboarding process is to apply the technology that allows us to comply with KYC legislation without affecting the user experience and usability during the process, keeping the processes 100% digital, paperless and without the need to go in person to an office.
With our MobbScan technology, we not only enable a 100% digital and automated registration process, but we also allow biometric authentication of customers at a later stage with a focus on usability and user experience.
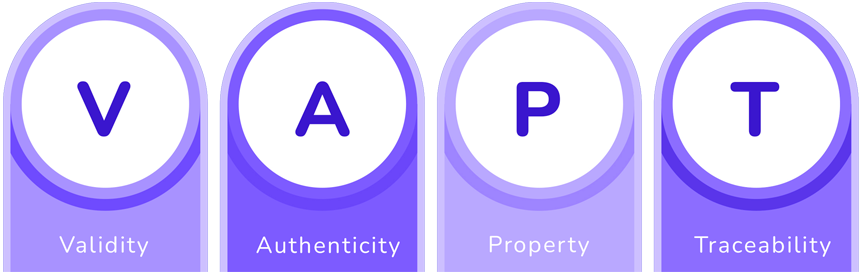
VAPT: Creating a digital identity in Digital Onboarding
What should we take into account from an ID document verification point of view when doing a Digital Onboarding process? Well, that’s what Mobbeel calls VAPT (Validity, Authenticity, Property and Traceability):
- Validity, since the document must be automatically detected and its information correct.
- Authenticity, so it is not a fake document.
- Property: the person who presents it is its legitimate holder.
- Traceability: we comply with the Know Your Customer / Anti-money Laundering regulations.
At SEPBLAC, (Spain’s Financial Intelligence Unit), you can find the main legal provisions regarding the prevention of money laundering and terrorist financing and capital movements and economic transactions with other countries. Regulations are classified into three areas:
Let’s move on to AML; what is AML, and how does it work?
AML stands for Anti-Money Laundering and refers to a set of regulations and procedures designed to prevent users and organisations from laundering illegally obtained money. As you may know, money laundering is the process of concealing the illicit origin of funds so that they appear legitimate.
The operation of AML involves the implementation of measures by financial institutions and other entities to detect and prevent such activities. It includes the detection of unusual or suspicious transaction patterns that could indicate money laundering activities, such as multiple transfers in a short time and the transfer of large amounts of money to newly created accounts.
Just as digital onboarding technology finds its place in KYC, there are technologies for AML prevention. Some of them are the following:
- Artificial intelligence: AI strengthens AML systems and trains them to adapt and learn in the face of new threats and crime patterns. AI, together with machine learning, automates the detection of suspicious transactions, constantly adjusting predictive models. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms can analyse large volumes of data to identify anomalous patterns of behaviour.
- Transaction monitoring tool: monitors financial transactions in real-time, identifying unusual behaviour. These types of solutions are configured to issue automatic alerts so that the staff in charge can take action.
- Risk management platform: assesses and classifies the risk associated with customers, transactions and locations.

So, what is the relationship between KYC and AML?
KYC acts as the starting point for compliance with AML regulations. Before establishing a business relationship with a customer, financial institutions must perform KYC procedures to verify their identity. It involves collecting information on identity, job position, source of funds and purpose of the business relationship. The information obtained during the KYC process is essential to ensure that customers are legitimate and to establish a reliable database.
Once a business relationship has been established through the KYC process, financial institutions continuously monitor transactions to detect possible money laundering activities.
KYC and AML complement each other in risk management.
Main differences between KYC AML
Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering are related but distinct concepts.
The main difference is that KYC focuses on verifying the identity of customers and seeks to know who the users are with whom a financial institution has relationships. In contrast, AML focuses on the prevention of illicit economic activities and includes measures and procedures to identify, monitor and report suspicious activities.
Another clear difference is that AML applies not only at the stage of remote customer onboarding but also throughout the legal relationship.
KYC/AML regulations
Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering regulations are local and differ from country to country, the same being true for your jurisdiction.
Europe
Since 2016, Europe has passed three AML Directives (AML4, AML5 and AML6), all of which extend the scope of KYC requirements to new sectors and the need for more stringent customer due diligence. These processes include the collection, verification and record keeping of personally identifiable information (PII) and the screening of customers against sanctions, international lists and adverse notices.
Furthermore, eIDAs2 and PSD3 (Payment Services Directive 3) will lead to cross-border digital identity, enhanced protection of consumer rights and improved competition in the payments industry.
Spain
In Spain, we have Law 10/2010 of 28 April on the prevention of money laundering and terrorist financing.
Within the financial system, SEPBLAC is the supervisory authority for the prevention of money laundering and the prevention of terrorism. At the same time, in the Gambling industry, the DGOJ (Dirección General de Ordenación del Juego) is responsible for issuing various resolutions regulating gambling activity.
It is also important to mention the Commission for the Prevention of Money Laundering and Monetary Offences (CPBCIM), a body in charge of supervising and regulating activities related to the prevention of money laundering and monetary offences. The main goal of this Commission is to develop policies, establish regulations and coordinate actions to prevent and combat money laundering and other illicit financial activities. The Commission is a body under the Ministry of Economy and Business Support. It works closely with SEPBLAC to ensure compliance with regulations and promote the integrity of the financial system.
It is no secret that due to its geographical location, Spain is a natural hub between Europe, Africa and Latin America, which has made it a gateway for all kinds of illicit activities related to drug trafficking, as well as a European hub for money laundering.
As a consequence, a large part of the profits from drug trafficking were invested in the purchase of real estate during the real estate bubble in coastal areas. This situation led to the introduction of money laundering prevention policies at the end of the 1980s.
Some of the companies affected by KYC/AML regulations in Spain are:
- Bank
- Mutual savings banks
- Credit companies
- Insurance companies
- Financial advisors
- Stockbrokers and securities firms
- Pension fund managers
- Collective investment schemes
- Postal services
- Currency exchange bureaux
- Non-official financial institutions and persons exchanging or transmitting money
- Real estate agents
- Dealers in precious metals, precious stones, antiques and art
- Legal advisers and lawyers
- Accountants
- Auditors
- Notaries
- Casinos and gambling houses
- Real estate agents

International cooperation importance
AML has become increasingly important in the financial world due to the globalisation of economic activities and the sophistication of the methods used by criminals to launder money. Therefore, international cooperation has become essential due to the transnational nature of money laundering. Offenders often move funds across multiple jurisdictions to conceal their illicit origin. Cooperation facilitates the exchange of information, the coordination of investigations, and the establishment of international standards to prevent and detect money laundering effectively.
International anti-money laundering bodies
Intergovernmental bodies such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) exist to make international cooperation effective. FATF standards and promotes the effective implementation of policies and measures to combat money laundering globally. At the same time, it sets itself up as a regulatory body, carrying out actions to legislate and establish regulations in collaboration with the state authorities of each country.
One of its main initiatives is the creation and adoption of the FATF Recommendations, which ensure a coordinated global response to combat corruption, money laundering and terrorist financing.
Within the global network of Financial Action Task Forces, there are two groups:
- The Latin American Financial Action Task Force (GAFILAT) is a regional intergovernmental organisation created to combat money laundering and terrorist financing in Latin America. It works to promote effective policies and measures to prevent and combat money laundering and terrorist financing in the region. It includes the assessment of national systems to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing, as well as technical cooperation and capacity building to help member countries strengthen their regulatory and enforcement frameworks.
- The Caribbean Financial Action Task Force (CFATF), on the other hand, focuses specifically on the Caribbean region. Like GAFILAT, it aims to combat money laundering, conduct assessments of national systems to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing, and provide technical assistance to territories in the region.
The European Supervisory Authorities are independent bodies of the European Union (EU) responsible for supervising the financial sector in specific areas, such as banking, insurance and securities markets. These authorities, which include the European Banking Authority (EBA), the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), aim to ensure the stability and efficiency of the European financial system. They work together with national regulators to set common standards, promote cross-border cooperation and protect the interests of financial consumers across the EU.
What is the future of KYC AML processes?
The future of KYC/AML processes will have a customer experience focus with increasingly intelligent and robust solutions. Some of the global KYC and AML trends will be:
- Improved customer experience: processes will be simplified and become more transparent, making it easier for customers to complete KYC/AML requirements. Guided options with retries will be implemented, improving conversion rates and reducing friction.
- More robust and intelligent controls: using advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning allows the detection of suspicious behaviour patterns more effectively. Workflows will be more adaptive and flexible and can be adjusted according to the needs and risks associated with each customer and transaction.
- Cross-device options with QR redirects: cross-device options are here to stay to provide a more usable experience, allowing customers to initiate and complete KYC/AML processes on different devices. This way, thanks to QR redirections, it will be possible to start the process on the desktop and move to the mobile option with a quick transition.
The KYC/AML solution that we have in Mobbeel allows us to verify the identity of a customer by automatically scanning their identity document with facial biometrics and liveness detection in web and mobile environments, validating their identity, extracting the information using OCR and complying with international regulations such as the provisions of SEPBLAC by introducing unassisted videoconferencing for financial institutions.
If you are interested in our technology do not hesitate to contact us, and if you liked the article, share it and add value to your followers!

I’m a Software Engineer with a passion for Marketing, Communication, and helping companies expand internationally—areas I’m currently focused on as CMO at Mobbeel. I’m a mix of many things, some good, some not so much… perfectly imperfect.

GUIDE
Fully know your customers and drive the growth of your business
The journey between an organisation and its clients begins with proper verification, ensuring the safety of both parties. This KYC guide is essential for understanding the importance of knowing your users and complying with legal requirements.




