In an increasingly interconnected digital world, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring secure access to online services is of paramount importance. Multifactor Authentication (MFA), also known as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), is a security protocol that introduces an extra level of validation beyond the conventional username and password.
Thus, in the evolving landscape of digital security, integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with biometrics proves to be an ideal match. The unique characteristics of biometric traits, coupled with convenience, heightened resistance to attacks, and improved user experience, position biometrics as a strong and secure component in the MFA process.
By leveraging the inherent strengths of biometrics, companies and organizations can enhance the security of their systems, protect user accounts, and build trust in an increasingly digital world.
What is Multifactor Authentication (MFA)?
Multifactor Authentication (MFA), is a security mechanism that adds an additional layer of verification to the traditional username and password combination. It requires users to provide two or more pieces of evidence to prove their identity when accessing an account or platform.
The goal of MFA is to enhance security by making it more difficult for fraudsters to gain access, even if they manage to obtain or guess the user’s password.
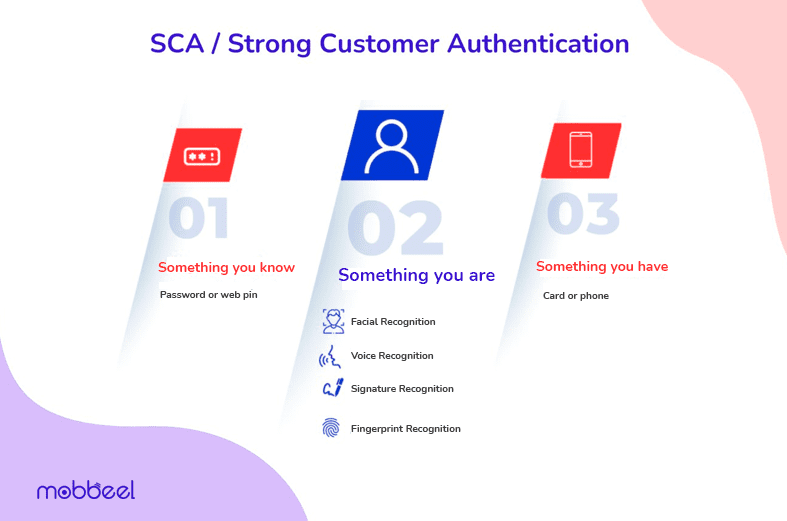
MFA or Multifactor Authentication typically involves three different factors or categories of authentication:
- Something You Know: This factor involves knowledge-based authentication, where the user must provide information that only they should know, such as a password, PIN, or the answer to a secret question.
- Something You Have: This factor refers to possession-based authentication, where the user must possess a physical item or device to complete the authentication process. It could be a mobile phone, hardware token, smart card, or a one-time password (OTP) generated by an authentication app.
- Something You Are: This factor uses biometric-based authentication, relying on the user’s unique physical or behavioral features. Biometric data, such as face recognition, fingerprints, iris scans, or voice recognition, is used to verify the user’s identity.

To authenticate using Multifactor Authentication or MFA, the user typically provides their initial credentials (username and password) as the first factor. Then, they are prompted to provide the second factor, which could be a verification code sent to their registered mobile device, a face recognition verification, or any other form of additional verification.
By combining multiple factors, MFA significantly strengthens security because an attacker would need to possess more than just the user’s password to gain unauthorized access. Even if one factor is compromised, the additional factors act as a barrier to prevent the fraud.
MFA (Multifactor Authentication) has become increasingly popular and is widely adopted by various online platforms, banking institutions, email providers, and other services that prioritize security. It provides an effective means to protect user accounts and sensitive information, reducing the risk of identity theft, data breaches, and other security incidents
What is Two Factor Authentication?
Two Factor Authentication (2FA) is another term used to refer to the same security mechanism as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). It is a method of verifying a user’s identity by requiring them to provide two distinct pieces of evidence or factors.
To complete the Two-Factor Verification process, the user first enters their initial credentials (username and password) as the first factor. Then, they are prompted to provide the second factor, which could be a biometric verification, a OTP code sent to their mobile device or a physical token to be inserted.
Two-Factor Verification is an effective security measure that helps mitigate the risks associated with password breaches, phishing attacks, and credential theft.
What is the difference between MFA and 2FA?
MFA (Multifactor Authentication) and 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) are terms that are often used interchangeably, and the difference between them can be a matter of terminology or context. However, there is a subtle distinction that can be made between the two:
- MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): MFA refers to an authentication method that requires users to provide two or more factors of authentication from different categories. These categories typically include “something you know,” “something you have,” and “something you are.” MFA encompasses the broader concept of using multiple factors for authentication, which can include more than two factors.
- 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication): 2FA is a specific subset of MFA and refers specifically to the use of two distinct factors for authentication between “something you know” (such as a password), “something you have” (such as a verification code sent to a mobile device) or “something you are” (biometrics).
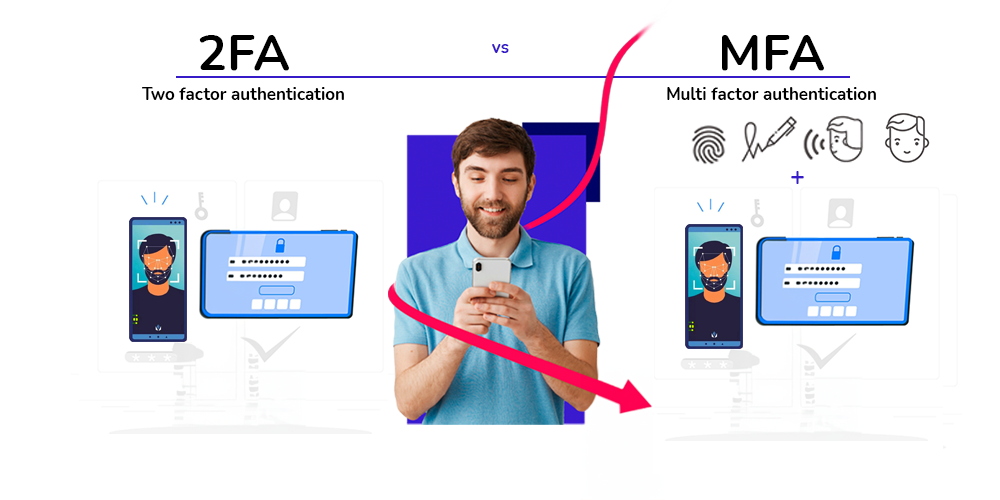
![]() In essence, 2FA is a type of MFA that specifically requires two factors, whereas MFA can involve more than two factors.
In essence, 2FA is a type of MFA that specifically requires two factors, whereas MFA can involve more than two factors.
However, the terms MFA and 2FA are often used interchangeably in practice, and the important aspect is the use of multiple factors to enhance security.
It’s worth noting that the specific terminology may vary depending on the context or industry. Some organizations or service providers may use “2FA” to refer to the broader concept of using multiple factors, while others may use “MFA” to describe the use of two factors.
Ultimately, the goal remains the same: to strengthen security by requiring users to provide additional evidence beyond just a password.
What are two factor authentication best practices?
Implementing Twofactor Authentication (2FA) using best practices can enhance the security posture of your platform or service while ensuring a positive and smooth user experience. Let’s highlight some key best practices for implementing and managing 2FA:
Enable 2FA by default
Make 2FA available to all users and encourage them to enable it during the account setup process. By making it the default option, you promote security from the start and increase the adoption rate. In the European open banking industry, strong customer authentication (SCA) based on two-factor authentication is mandatory since the implementation of the PSD2 regulation.
Offer multiple 2FA methods
Provide users with a range of 2FA methods to choose from, such as biometric authentication, SMS verification codes, authentication apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy), hardware tokens or email-based verification. Offering flexibility allows users to select the method that suits them best.
Educate users
Provide clear and concise instructions on how to set up and use 2FA. Create user-friendly guides, FAQs, or video tutorials to help users understand the importance of 2FA and how to enable it. Emphasize the added security and encourage adoption.
Consider backup options
In case a user loses access to their primary 2FA method (e.g., a lost or damaged phone), offer backup options like biometrics, backup codes, secondary email addresses, or phone number verification as alternatives to regain access to their account. In fact, biometric authentication is a great solution for password recovery since it offers a streamline and seamless way to recover it.
Allow remembered devices
For convenience, consider allowing users to designate trusted devices or browsers that are exempt from 2FA for a specified period. This reduces the need for repeated authentication on trusted devices while still enforcing it on unfamiliar devices or new logins.
Monitor and notify
Implement monitoring systems to detect unusual or suspicious account activity. Send notifications to users when 2FA is triggered or when changes to their 2FA settings are made, such as enabling or disabling 2FA or adding new devices.
Regularly review and update
Periodically review your 2FA implementation and the available methods to ensure they align with current security standards. Stay updated on the latest authentication technologies, vulnerabilities, and best practices to adapt and improve your approach.
Simplicity and usability
Strive for a simple and intuitive user experience when enabling and using 2FA. Minimize friction and steps required during the authentication process, making it easy for users to adopt and use 2FA effectively.
Employee education
If you’re implementing 2FA within a company, educate employees on the importance of 2FA and provide training on how to set it up and use it correctly. Regularly reinforce the significance of 2FA as part of the company’s security culture.
Continuously promote security awareness
Incorporate ongoing security awareness and education initiatives to remind users about the importance of 2FA and reinforce good security practices.
The perfect match: Why biometrics fit perfectly in a 2FA process
Passwords, once considered sufficient, are increasingly vulnerable to breaches and attacks. As a result, the integration of Multifactor Authentication (MFA) has gained prominence, with biometrics emerging as a perfect match for enhancing security in the 2FA process. Biometrics offer several advantages that make them an ideal fit for bolstering the security of online accounts and services.
Uniqueness and inherent security
Biometric features, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voiceprints, are inherently unique to individuals. Unlike passwords or tokens, which can be forgotten, lost, or stolen, biometric characteristics are difficult to replicate or forge. Leveraging biometrics as one of the factors in the 2FA process adds an extra layer of security by binding authentication to an individual’s physical attributes.
Convenience and user experience
Biometric authentication methods offer a seamless and user-friendly experience. Users can authenticate themselves simply by providing a fingerprint scan, facial recognition, or a voice sample to be authenticated by voice biometrics.
Compared to remembering and typing passwords or carrying physical tokens, biometrics streamline the authentication process and eliminate the hassle associated with traditional methods. This convenience encourages wider adoption of 2FA and reduces user resistance to implementing additional security measures.
Improved resistance to attacks
Biometrics provide enhanced resistance against various attack vectors. Biometric features are not easily guessed or replicated, reducing the likelihood of successful brute-force attacks. Additionally, biometric systems often employ advanced algorithms to detect and prevent spoofing attempts, such as presenting a manipulated face image. These measures strengthen the overall security of the 2FA process, safeguarding user accounts against fraudulent access.
Continuous authentication and user presence
Biometric authentication can facilitate continuous user verification throughout a session. For example, on devices equipped with fingerprint scanners or facial recognition cameras, users can be periodically prompted to authenticate themselves, ensuring that the approved user remains present during the entire session.
Integration with existing devices
Biometric technologies have become increasingly ubiquitous in modern devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Leveraging these built-in biometric sensors or cameras for 2FA eliminates the need for additional hardware tokens or devices. Users can leverage the biometric capabilities of their existing devices, making the adoption of 2FA more convenient and cost-effective.
The FIDO2 Standard allows users to use their own devices to easily authenticate to online services, in both mobile and desktop environments.
However, in certain industries such as the financial industry, the use of mobile biometrics as a strong authentication mechanism (SCA) is not recommended.
Privacy and compliance considerations
Biometric data can offer an added layer of privacy compared to traditional authentication methods. While passwords can be intercepted or stolen, biometric data generally remains locally stored on the user’s device or securely encrypted on servers, minimizing the risk of exposure. Furthermore, biometric authentication aligns with privacy regulations, as the biometric templates used for authentication are non-reversible.
PSD2: 2FA for strong customer authentication
PSD2, which stands for the Second Payment Services Directive, is a regulatory framework implemented by the European Union to promote innovation, competition, and security in the payment services industry. The directive aims to provide consumers with enhanced protection and control over their financial data while fostering an open and integrated European payments market.
One of the key aspects of PSD2 is the requirement for Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), which aligns with the principles of 2FA.
The purpose of SCA is to ensure that customers’ electronic payments are authenticated through the use of at least two independent factors to enhance security.
Under PSD2, 2FA is a critical component for securing customer transactions and access to payment accounts. It mandates the use of two or more authentication factors to verify the customer’s identity when initiating electronic payments or accessing account information.
These factors can include something the customer knows (e.g., a password or PIN), something the customer possesses (e.g., a mobile device or smart card), or something inherent to the customer (e.g., biometric data).
The introduction of 2FA in PSD2 helps combat fraud and provides an additional layer of protection against identity theft and fraudulent transactions. It adds an extra level of security beyond traditional password-based authentication, reducing the risk of account compromise and enhancing consumer trust in online payment services.
Furthermore, the combination of PSD2 and 2FA fosters an environment where third-party providers (TPPs) can securely access payment accounts with the explicit consent of the account holders. These TPPs, known as Account Information Service Providers (AISPs) and Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs), must also adhere to the authentication requirements set forth by PSD2, including the use of 2FA, to ensure secure and authorized access to customer accounts and transactional data.
Strengthening security and trust: Multifactor Authentication based on KYC standards
Multifactor Authentication (MFA) based on KYC standards offers a robust and comprehensive approach to secure authentication in the digital realm. By verifying customer identities through KYC principles and implementing multiple authentication factors, companies can strengthen security, comply with regulatory requirements, and foster trust with their customers.
Furthermore, The use of KYC solutions enables the generation of credentials for future platform access.
This powerful combination ensures that only approved individuals gain access to sensitive information and helps protect against identity theft, fraud, and malicious activities. Embracing MFA based on KYC standards is a crucial step towards creating a secure, compliant, and customer-centric environment in the digital era.
Mobbeel: biometric solutions for 2FA / MFA – Multifactor Authentication
Biometrics has become an essential component in two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) processes, playing a crucial role in securing digital identity. MobbID provides different biometric authentication methods, such as face recognition and voice biometrics.
The biometric face or voice template are challenging attributes to replicate, which significantly reduces the risk of impersonation or presentation attacks. This biometric uniqueness strengthens authentication, as users must provide something inherent to themselves beyond what they may know or possess.
MobbID has been designed to easily integrate with other solutions when you need to add biometric identification and verification.
With our wide range of native or web SDKs, as well as a restful API, you will be able to include state-of-the-art biometric technology in your applications, ERP, or business procedures when enforcing any identity verification with biometrics.
Feel free to reach out if you want to balance positive customer experience and security with a highly tested biometric identification method.

I’m a Software Engineer with a passion for Marketing, Communication, and helping companies expand internationally—areas I’m currently focused on as CMO at Mobbeel. I’m a mix of many things, some good, some not so much… perfectly imperfect.

PRODUCT BROCHURE




